Friday, October 31, 2014
IR Remote Transmitter Receiver
| IR Remote - Transmitter |
| IR Remote Receiver |
300 Watt MOSFET Broadband Amplifier Using MRF141G

I recommend getting the two transformer assemblies, instead of trying to create them, due to the fact 15-ohm hardline is not straightforward to come across.
Outdoor Lighting Controller Circuit Diagram
Outdoor Lighting Controller Circuit Diagram :
The circuit is star ted by closing switch (or pushbutton) S1. The lamp then immediately receives power via the bridge rectifier. The drop across diodes D5 to D10 is 4.2 V, which provides the power supply for the delay circuit itself, built around the CD4060 binary counter.
When the switch is opened the lighting sup-ply current continues to flow through Tri1. The NPN optocoupler in the triac drive circuit detects when the triac is active, with antiparallel LED D1 keeping the drive sym-metrical. The NPN phototransistor inside the coupler creates a reset pulse via T1, driving pin 12 of the counter. This means that the full time period will run even if the circuit is retriggered. The CD4060 counts at the AC grid frequency. Pin 3 goes high after 213clocks, which corresponds to about 2.5 minutes. If this is not long enough, a further CD4060 counter can be cascaded. T2 then turns on and shorts the internal LED of opto-triac IC2; this causes Tri1 to be deprived of its trigger current and the light goes out. The circuit remains without power until next triggered.
The circuit is only suitable for use with resistive loads. With the components shown (in particular in the bridge rectifier and D5 to D10) the maximum total power of the connected bulb(s) is 200 watts. As is well known, the filament of the bulb is most likely to fail at the moment power is applied. There is little risk to Tri1 at this point as it is bridged by the switch. The most likely consequence of overload is that one of diodes D1 to D6 will fail. In the prototype no fuse was used, as it would not in any case have been easy to change. However, that is not necessarily recommended practice!
Circuits at AC line potential should only be constructed by suitably experienced persons and all relevant safety precautions and applicable regulations must be observed during construction and installation.
Author : Harald Schad - Copyright : Elektor
Thursday, October 30, 2014
What is The Parallel Resonance Circuit





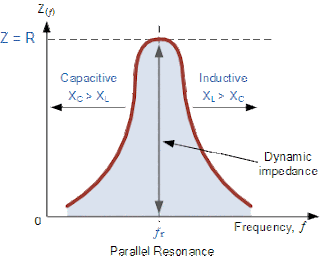

Current in a Parallel Resonance Circuit


Bandwidth & Selectivity of a Parallel Resonance Circuit
Parallel Resonance Tutorial Summary
Resonant Frequency using Impure Components
Project Mini RS232 Data Switch Circuit Diagram
Mini Stereo Power Amplifier using TDA2822
| Mini Stereo Power Amplifier using TDA2822 Circuit Diagram |
On Demand WC Fan Using 555 Circuit Diagram
Wednesday, October 29, 2014
Fog Lamp Sensor Circuit Diagram
Variable DC Power Supply with 2N3055 This is variable power supply for multi purpose usage and very useful to supply your electronic tools or your pro
Variable DC Power Supply with 2N3055
Components:
P1____________500R Linear PotentiometerNotes:
P2_____________10K Log. Potentiometer
R1,R2__________2K2 1/2W Resistors
R3____________330R 1/4W Resistor
R4____________150R 1/4W Resistor
R5______________1R 5W Resistor
C1__________3300µF 35V Electrolytic Capacitor (see Notes)
C2_____________1µF 63V Polyester Capacitor
D1,D2_______1N5402 200V 3A Diodes
D3____________5mm. Red LED
Q1___________BC182 50V 100mA NPN Transistor
Q2___________BD139 80V 1.5A NPN Transistor
Q3___________BC212 50V 100mA PNP Transistor
Q4 _________2N3055 60V 15A NPN Transistor
T1____________220V Primary, 36V Center-tapped Secondary
50VA Mains transformer (see Notes)
PL1___________Male Mains plug
SW1___________SPST Mains switch
- P1 sets the maximum output current you want to be delivered by the power supply at a given output voltage.
- P2 sets the output voltage and must be a logarithmic taper type, in order to obtain a more linear scale voltage indication.
- You can choose the Transformer on the grounds of maximum voltage and current output needed. Best choices are: 36, 40 or 48V center-tapped and 50, 75, 80 or 100VA.
- Capacitor C1 can be 2200 to 6800µF, 35 to 50V.
- Q4 must be mounted on a good heatsink in order to withstand sustained output short-circuit. In some cases the rear panel of the metal box in which you will enclose the circuit can do the job.
- The 2N3055 transistor (Q4) can be replaced with the slightly less powerful TIP3055 type.
Triangle Square Wave Oscillator Circuit Diagram
Equalising HEXFETs
Tuesday, October 28, 2014
Mini 2x75W Stereo Power Amplifier
Standard Microcontroller
Two Colour LED Light Bar Circuit
Eight Band Sub Woofer Graphic Equaliser
Monday, October 27, 2014
TDA2030 bridge 35 watt power amplifier Diagram Circuit
A very simple 35 watt power amplifier electronic project can be designed using the TDA2030 power audio IC. The TDA2030A is a monolithic IC in Pentawatt package intended for use as low frequency class AB amplifier.
The TDA2030A provides high output current and has very low harmonic and cross-over distortion. TDA2030 ICs connected in bridge mode.
This circuit require few external electronics parts and supports a 8 ohms load . This 35 watt power amplifier require a very good filtered DC power supply , that will provide an output voltage of +/- 16 volts .
Using this circuit you can design a very simple and efficiency subwoofer amplifier with a maximum output power of 35 watt power .
The device incorporates a short circuit protection system comprising an arrangement for automatically limiting the dissipated power so as to keep the working point of the output transistors within their safe operating area. Also a conventional thermal shut-down system is also included .
However a heatsink must be used for the TDA2030 bridge circuit but for any reason, if the junction temperature increases up to 150oC, the thermal shut-down simply reduces the power dissipation and the current consumption.
Very Simple Pre Regulator
LM4765 2 x 30 watt amplifier Diagram Circuit
A very simple 2 x 30 watt amplifier electronic circuit project can be designed using the LM4765 stereo audio amplifier IC capable of delivering typically 30W per channel of continuous average output power into an 8Ω load with less than 0.1% THD+N.
This 2 x 30 watt amplifier electronic circuit is very simple and require few external electronic parts and can be used in high end stereo TVs or some other audio applications .
Each amplifier has an independent smooth transition fadein/out mute and a power conserving standby mode which can be controlled by external logic.
Like many other audio amplifier ICs the LM4765 has many features like Temperature protection circuitry, SPiKe protection ( means that these parts are safeguarded at the output against overvoltage, undervoltage, overloads, including thermal runaway and instantaneous temperature peaks).
This audio amplifier electronic circuit project can be powered from a wide input voltage range from 20 volt up to 66 volts , but typically is required a dual 28 volts input ( take care because |Vcc|+|Vee|<60 volts .
The audio IC must be mounted on a heat sink to keep the die temperature at a level such that the thermal protection circuitry does not operate under normal circumstances.
In this circuit diagram is represented just a part of the IC (one channel ) and numbers in parentheses represent pinout for amplifier B
VGA to BNC Adapter Converter Circuit and explanation
In this case the value of R2 should be reduced a little, but this has the side effect that the brightness noticeably decreases and the load on the graphics card increases. To keep the colour balance the same, the resistors for the other two colors (R1 en R3) have to be changed to the same value as R2. An EXOR gate from IC1 (74HC86) combines the separate V-sync and H-sync signals into a composite sync signal. Since the sync in DOS-modes is often inverted compared to the modes commonly used by Windows, the output of IC1a is inverted by IC1b. JP1 can then by used to select the correct operating mode. This jumper can be replaced by a small two-way switch, if required.
 |  |
 |  |
This switch should be mounted directly onto the PCB, as any connecting wires will cause a lot of interference. The PCB has been kept as compact as possible, so the circuit can be mounted in a small metal (earthed!) enclosure. With a monitor connected the current consumption will be in the region of 30 mA. A 78L05 voltage regulator provides a stable 5 V, making it possible to use any type of mains adapter, as long as it supplies at least 9 V. Diode D2 provides protection against a reverse polarity. LED D1 indicates when the supply is present. The circuit should be powered up before connecting it to an active VGA output, as otherwise the sync signals will feed the circuit via the internal protection diodes of IC1, which can be noticed by a dimly lit LED. This is something best avoided.
Resistors:
R1,R2,R3 = 470Ω
R4 = 100Ω
R5 = 3kΩ3
Capacitors:
C1,C3,C5 = 47µF 25V radial
C2,C4,C6,C7,C10 = 100nF ceramic
C8 = 4µF7 63V radial
C9 = 100µF 25V radial
Semiconductors:
D1 = LED, high-efficiency
D2 = 1N4002
T1 = BS170
IC1 = 74HC86
IC2 = 78L05
Miscellaneous:
JP1 = 3-way pinheader with jumper
K1 = 15-way VGA socket (female), PCB mount (angled pins)
K2,K3,K4 = BNC socket (female), PCB mount, 75Ω
Sunday, October 26, 2014
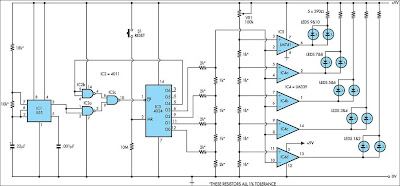
LED Lights circuits with LM339 IC555
Similar to the count has reached binary 1111, the then pulse sends the O4 output of IC3 high, which disables IC2c and IC3 stops together with. The four used outputs of IC3 are connected to a resistor ‘ladder’ which acts because a undemanding digital to analog convert-er (DAC). As the count increases so does the voltage produced by the top of the ladder and this is connected to the inverting inputs of four comparators inside IC4 (an LM339) and to IC5, which is a 741 op amp besides connected for instance a comparator.
The certain inputs of the comparators are connected to the taps of a voltage barrier, with the drumming voltages frozen using VR1, a 100kO trimpot. As IC3 counts, the rising stepped voltage from the DAC ladder switches the comparators on during sequence, preparatory with IC4d and working up to IC5. because each one comparator is bowed on, its put together of LEDs is lit; essential LEDs 1 & 2, so therefore LEDs 3 & 4 and so on. at what time all five pairs of LEDs are lit, the after that pulse from IC1 moves the binary count of IC3 to 10000, so the DAC voltage drops back to zip and all LEDs are extinguished. by the same age, plus additionally stops, as the lofty on O4 causes IC2c to mass expand gate pulses. The circuit it follows that remains stationary until the counter is reset by burning pushbutton switch S1. This allows a new-fangled sequence to kick off.
Saturday, October 25, 2014
Energy Saver Relay Coil Diagram Circuit
Circuit diagram:
The action of C2 causes the full supply voltage to appear briefly across the relay coil, which helps to activate the relay as fast as possible. Via T2, a delay network consisting of C1 and R2 controls the relay coil current flowing through T1 and R3, effectively reducing it to half the ‘pull in’ current. Diode D2 discharges C1 when the control voltage is Low. Around one second will be needed to completely discharge C1. T2 shunts the bias current of T1 when the delay has elapsed. Diode D1 helps to discharge C1 as quickly as possible. The relay shown in the circuit was specified at 12 V / 400 ohms. All component values for guidance only.
IC TLC271 Single supply Function Generator
The circuit has both square-wave and triangle-wave output. The left section is similar in function to a comparator circuit that uses positive feedback for hysteresis. The inverting input is biased at one-half the Vcc voltage by resistor R4 and R5. The output is fed back to the non-inverting input of the first stage to control the frequency.
The amplitude of the square wave is the output swing of the first stage, which is 8V peak-to-peak. The second stage is basically an op amp integrator.